Ever wonder if an air purifier produces heat when it is operating? Many homeowners worry about prospective increases in temperature or energy use, which is a typical issue. This article will examine whether air purifiers produce heat while they are functioning and will arm you with the knowledge you need to decide whether to use one in your home. So let’s get started and discover the answer to this urgent query!
Understanding Air Purifiers
Air purifiers are tools used to enhance indoor air quality by eliminating pollutants and toxins. They function by filtering out dangerous elements including germs, viruses, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), as well as airborne particles like dust, pollen, pet hair, and smoke. For anyone with allergies or respiratory issues, air purifiers are especially important in maintaining a clean and healthy environment.
Definition and Function
Appliances that use various technologies to enhance indoor air quality are called air purifiers or air cleaners. They frequently have fans, filters, and other systems to collect and get rid of airborne pollutants. An air purifier’s primary job is to purify the air by eliminating contaminants and enhancing air flow in general.
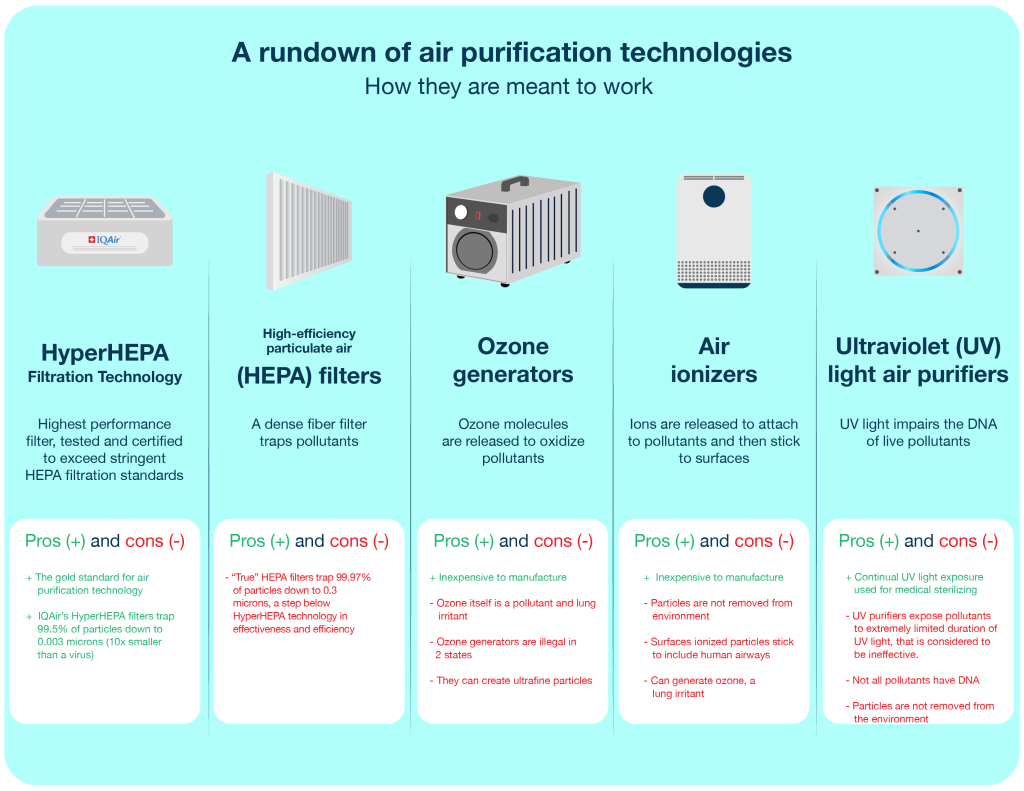
Popular Types of Air Purifiers
There are many various kinds of air purifiers on the market, and they all clean the air in a different way. Popular varieties include the following:
High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) Purifiers
HEPA air purifiers are very good at eliminating minute airborne pollutants. For the purpose of capturing particles as fine as 0.3 microns, they employ a dense fiberglass filter. People with allergies or asthma can find relief from common allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander thanks to HEPA filters.
Activated Carbon Purifiers
Air purifiers with activated carbon are made to get rid of gases, pollutants, and smells. These air purifiers have activated carbon filters that catch smoke, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and foul odors, making the air cleaner and fresher.
Ozone Generators
To get rid of odors and kill bacteria and mold, ozone generators produce the highly reactive gas ozone. They are debatable, though, and prolonged indoor use is not advised because ozone at high concentrations can be hazardous to people’s health.
Ionic Air Purifiers
Ion air purifiers use charged ions to attract airborne particles, making them adhere to surfaces or gather on metal plates inside the machine. They may create ozone as a byproduct, comparable to ozone generators, despite the fact that they can efficiently remove bigger particles like dust and pet hair.
UV-C Air Purifiers
Ultraviolet light is used by UV-C air purifiers to destroy bacteria, viruses, and other microbes. These air purifiers are frequently used in healthcare facilities and can help stop the transmission of airborne diseases.
Importance of Air Purifiers in Indoor Spaces
Numerous toxic contaminants, such as allergens, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and dangerous germs or viruses, can be found indoors. Allergies, respiratory problems, and other health disorders can be brought on by these toxins. With the aid of air purifiers, indoor air becomes cleaner and healthier to breathe. They can enhance general quality of life, particularly for those with allergies or respiratory disorders.
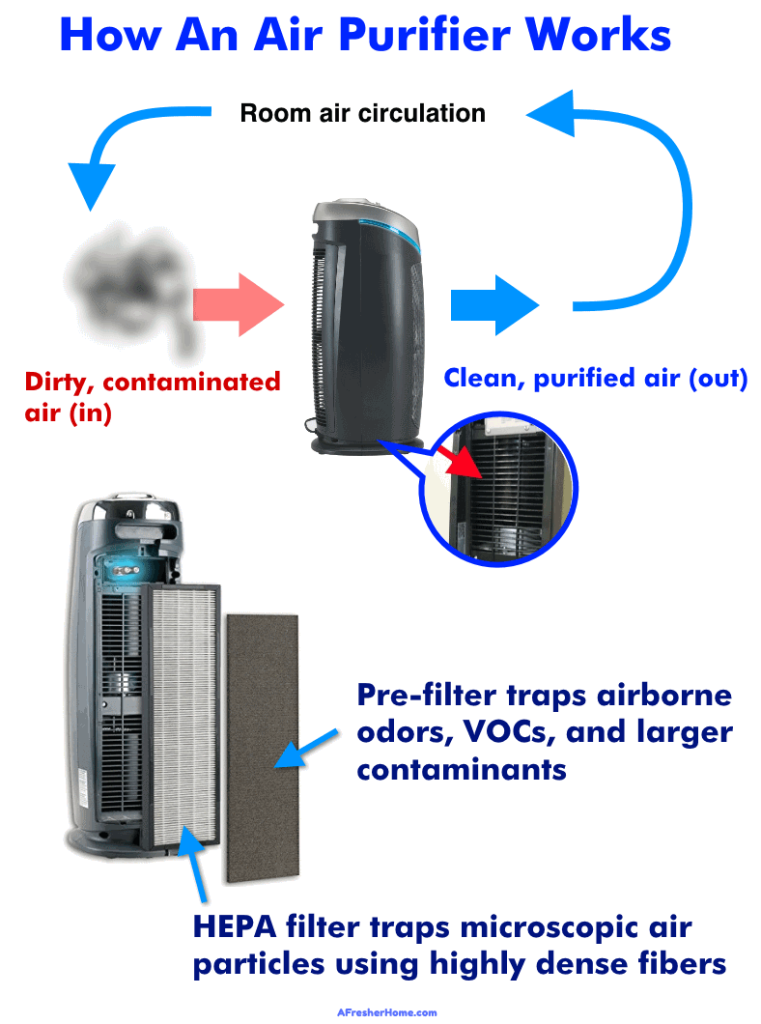
Mechanism of Air Purifiers
It is crucial to look at the mechanism of functioning of air purifiers in order to comprehend the components affecting heat generation. Filtration, circulation, and power source and energy consumption make up the three primary parts of an air purifier.
Filtration Process
A key part of air purifiers is the filtration process. Filters are made to catch and remove dust, pollen, and other contaminants from the air as it flows through the apparatus. The kind and effectiveness of the filter an air purifier uses can have a big impact on how well it cleans the air and produces heat.
Fan and Circulation
Fans are included with air purifiers to help move air across a space. Air from the surroundings is drawn in and forced through the filters with the aid of the fan. The purifier’s effectiveness is maximized by air circulation, which makes sure that a sufficient amount of air goes through the filtration process.
Power Source and Energy Consumption
A power source is necessary for air purifiers to function. The majority of air purifiers are made to plug into a regular electrical socket. An air purifier’s energy usage might change depending on its size, filtration system, and extra functions. To reduce heat generation and energy consumption, it is crucial to take an air purifier’s energy efficiency into account.
Factors Influencing Heat Generation
The quantity of heat produced by an air purifier might vary depending on a number of variables. To ensure peak performance and reduce any potential heat-related difficulties, it is essential to take these variables into account when choosing an air purifier.
Type of Air Purifier
Different kinds of air purifiers produce heat at different intensities. For instance, compared to HEPA and activated carbon purifiers, air purifiers using ozone-generating technology or UV-C light may produce greater heat. It is crucial to pick an air purifier that best satisfies the user’s unique requirements and preferences while taking potential heat generation into account.
Design and Size
An air purifier’s size and design both have an effect on how much heat it produces. In comparison to bigger or poorly built machines, compact air purifiers with effective cooling systems may produce less heat. It is advised to pick an air purifier with efficient heat dissipation mechanisms in addition to one that satisfies the specified air cleaning criteria.
Filtration System
The air purifier’s filtering technology may have an impact on how much heat it produces. For instance, HEPA filters can offer excellent air cleansing but may also limit airflow and increase heat production. Filters made of activated carbon are less constrictive and may produce less heat. Analyzing an air purifier’s potential for generating heat requires an understanding of its filtering technology.
Fan Speed and Power Settings
Heat generation can also be influenced by an air purifier’s fan speed and power settings. Increased airflow and better air cleaning performance are frequently the results of using higher fan speeds and power settings. They might, however, also result in increased heat production. By selecting the proper fan speed and power settings based on unique demands and preferences, it is crucial to achieve a balance between air cleaning effectiveness and heat generation.

Heat Generation in Different Air Purifiers
Heat generation varies across various types of air purifiers. Users can choose wisely depending on their unique requirements by understanding the heat generating characteristics of various devices.
High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) Purifiers
Due to the restricted airflow, HEPA purifiers with their dense fiberglass filters could produce some heat. However, the overall heat produced by HEPA purifiers is usually insignificant and shouldn’t be too uncomfortable.
Activated Carbon Purifiers
Compared to HEPA purifiers, activated carbon purifiers often generate less heat. Activated carbon air purifiers are primarily designed to remove gases, pollutants, and odors from the air, effectively purifying it while producing very little heat.
Ozone Generators
Ozone producers can produce a lot of heat while they create ozone. However, due to potential health hazards from high ozone levels, these devices are not advised for prolonged indoor usage. Before considering the use of ozone generators, it is imperative to comprehend the heat generation and health concerns.
Ionic Air Purifiers
Due to the utilization of ions to charge airborne particles, ionic air purifiers typically produce little heat. However, a little quantity of ozone produced as a byproduct by some ionic air purifiers may be a factor in heat production. Before making a purchase, it is crucial to take into account the heat and ozone emission of these appliances.
UV-C Air Purifiers
UV-C air purifiers employ ultraviolet light to destroy bacteria and viruses, possibly generating very little heat in the process. These air purifiers, which are frequently used in healthcare facilities, can efficiently enhance air quality without emitting a lot of heat.
Potential Heat-related Issues and Solutions
Although there is often little heat creation in air purifiers, there are some potential heat-related problems that consumers should be aware of. A secure environment can be ensured by properly recognizing and handling these problems.
Heat Emission in Small Spaces
The heat produced by an air purifier may be more noticeable and perhaps uncomfortable in cramped or poorly ventilated areas. It’s crucial to keep an eye on the temperature in these areas and think of alternate options if it gets too hot, such employing several smaller air purifiers or moving the device to a bigger place.
Heat-related Discomfort
Despite the fact that air purifiers don’t generate much heat, some people may be more sensitive to temperature changes and may feel uncomfortable. To lessen any potential discomfort, it is important to select an air purifier with effective cooling mechanisms and take into account user comfort preferences, such as changeable fan speeds or power settings.
Impact on Energy Efficiency
Although air purifiers are intended to enhance indoor air quality, they do use electricity while in use. Air purifiers’ energy usage might change depending on variables including fan speed, power settings, and other functions. To reduce energy consumption and potential heat generation, it is critical to select energy-efficient models and modify power settings according to individual demands.
Heat Build-up and Airflow
The heat that air purifiers produce may change the airflow patterns in a room by raising the ambient temperature. It is wise to think about where to put the air purifier in the space to maintain optimum airflow and avoid stagnant spots. The air purifier’s effectiveness can be improved by strategically positioning it away from obstructions to maximize airflow.

Optimizing Air Purifier Usage
Certain procedures can be followed to optimize the advantages of an air purifier and prevent any potential heat-related problems.
Proper Placement
It is essential to set an air purifier correctly in order to maximize effectiveness and reduce heat production. It is best to position the air purifier away from barriers like walls or furniture, in a space with enough ventilation. This lessens the possibility of heat accumulation while enabling optimum circulation and effective air cleaning.
Regular Maintenance
For the appliance to work at its best and last as long as possible, regular maintenance is necessary. This entails routine filter cleaning or replacement, as blocked or unclean filters may restrict airflow and perhaps increase heat generation. To keep the air purifier operating efficiently, adhere to the maintenance and cleaning instructions provided by the manufacturer.
Smart Features and Automation
Some air purifiers have automated features and other intelligent components that might help them operate more efficiently and generate less heat. Sensors that detect air quality levels and modify the purifier’s operation accordingly may be among these features. By using such features, you may clean the air effectively without producing extra heat.
Comparison with Other Heat-generating Appliances
It can be useful to contrast air purifier heat generation with that of other heat-generating devices that are frequently seen in indoor areas.
Air Conditioners
The purpose of air conditioners is to chill the air and keep indoor rooms at a reasonable temperature. Air conditioners produce cool air, but as a consequence of cooling, they also produce heat. Since air purifiers often produce less heat than air conditioners do, they are a good choice for improving indoor air quality without producing a lot of heat.
Space Heaters
During the colder months, space heaters are utilized to warm indoor rooms. Space heaters, as opposed to air purifiers, are made specifically to produce heat and have a high heat output. To avoid overheating and other safety risks, it is crucial to operate space heaters properly and to make sure there is adequate ventilation.
Electronics and Appliances
Computers, televisions, and refrigerators are just a few examples of the numerous gadgets and home equipment that produce heat when in use. Even though these appliances can produce a lot of heat, it usually stays inside the appliance and doesn’t affect the air’s temperature or quality. Even though they don’t produce much heat, air purifiers prioritize improving the quality of indoor air above creating more heat.

Efficiency vs. Heat Generation Trade-off
It’s crucial to take efficiency and heat production into account when choosing an air purifier. Higher efficiency purifiers could produce more heat and use more energy. On the other hand, models with lower energy usage can have a limited ability to clean the air. By achieving the ideal balance between energy economy and air cleaning effectiveness, heat generation can be reduced while performance is maintained.
Choosing Energy-efficient Models
Modern technologies are used by energy-efficient air purifiers to reduce energy consumption and potential heat generation, such as low-power consumption fans and optimized filtering systems. To find models that balance performance and energy savings, look for those that are Energy Star certified or have high efficiency ratings.
Finding the Right Balance
When selecting an air purifier, it’s crucial to strike the perfect balance between energy efficiency and air cleaning effectiveness. To choose the model that provides the desired balance between efficiency and heat generation, take into account variables such room size, particular air cleaning needs, and user preferences.
Heat Generation and Noise Levels
During operation, air purifiers may also generate heat and noise. Users can choose an air purifier more intelligently by understanding the relationship between heat and noise.
Relationship between Heat and Noise
In air purifiers, heat production and noise levels may be connected. Airflow may rise with higher fan speeds or power settings, which may result in more noise and heat production. When choosing an air purifier, it’s crucial to take the ideal balance between air cleaning effectiveness and noise levels into account.
Considering Noise Output
It is advisable to take into account both heat generation and noise output while assessing air purifiers. To ensure a cozy and quiet environment, look for models that have adjustable fan speeds and noise reduction capabilities. This makes it possible to effectively clean the air without compromising user comfort.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
There are a lot of untruths and misconceptions about how heat is produced by air purifiers. To provide a comprehensive understanding of the true impact of air purifiers, these myths should be dispelled.
Air Purifiers as Heating Devices
Contrary to popular perception, heater functions are not intended for use with air purifiers. Air purifiers’ main function is to clean the air and enhance the quality of the air indoors, while they can have a small impact on heat generation. They shouldn’t be used as your main source of heat.
Heat Mitigation Technologies
To reduce heat generation, some air purifiers use heat mitigation techniques including effective cooling systems or heat sinks. These technologies are intended to properly disperse heat and guarantee that the device’s overall temperature stays within a safe limit. To reduce the likelihood of heat-related problems, users should search for air purifiers with these cutting-edge characteristics.
Air purifiers are useful tools for enhancing indoor air quality and establishing a healthy living environment, to sum up. When choosing an air purifier, it’s crucial to take into account things like kind, design, filtration system, and power settings, even if they may produce little heat while operating. Users may make the most of air purifiers and benefit from clean, fresh air without feeling overly uncomfortable by understanding the mechanisms and potential heat-related problems.
Recommendations: BLUEAIR Air Purifier

